Notes
EXPLANATION OF THE RIGHTS OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION

Medication errors are one of the most common and dangerous medical errors that a nurse or midwife could commit. This is mostly because medication error can result in permanent disability or even death of the patient. It is very important that the nurse or midwife has adequate knowledge about the patient’s medication because they spend much time with the patient and they mostly administer these medications.
We have known about the traditional 5 R’s (Rights) of Drug administration which include: Right Patient, Right Drug, Right Time, Right Route, and Right Dosage. But over the years, more have been suggested through research to combat medication error.
THE 5 TRADITIONAL RIGHTS (R’s) OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION
RIGHT PATIENT: It is the responsibility of the nurse or midwife to ensure that patient being treated is, in fact, the correct recipient for whom medication was prescribed. Ask the patient’s full name even if you know the name already, confirming with medical wristbands if available. Check if the name matches with prescription, folder, or chart. Always make sure that you address the patient by their full name and not first name or surname alone. It is advisable not first name or surname alone as there could be patients with similar names. Also never forget to use two or more identifiers (Name, Assigned identification number (e.g., medical record number, NHIS Number), Date of birth, Phone number, Address, or Photo) which will be helpful in situations where different patients may have the same name.
RIGHT DRUG: The nurse or midwife must make sure that the medication being served is the same as the one prescribed. Some medications have similar spelling and sound but perform different functions and therefore the nurse must do due diligence in serving medications. It is also important to check for the expiry date of the medication. The nurse or midwife must inquire if the patient has any known allergies or history of an allergic response to a drug they are about to administer.
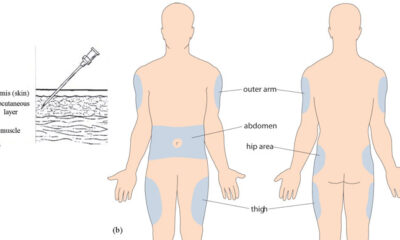
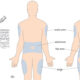
RIGHT ROUTE: Some common routes of drug administration includes oral, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intradermal, intravenous, sublingual, and topical. The routes of administration chosen to determine the time it takes to absorb the drug, time it takes for the drug to act, and potential side effects. It is very important for the nurse or midwife to be knowledgeable in the understanding of the physiology influencing drug absorption rates and time of drug onset, as these principles relate to medication administration. The nurse or midwife must also be up to date on new drugs as well as uncommonly used drugs. Find out if patients can tolerate the ordered route for the prescribed medication.
RIGHT TIME: As a nurse or midwife, always make sure the patient’s medication is administered the time it was intended by the prescriber. Double-check that you are giving the prescribed at the correct time and confirm when the last dose was given. To maintain the therapeutic effect, certain medications have specific intervals during which another dose should be given. A guiding principle of this ‘right’ is that medications should be prescribed as closely to the time as possible, and nurses should not deviate from this time by more than half an hour to avoid consequences such as altering bioavailability or other chemical mechanisms. It is very important especially, with intravenous medications that they are administered at the correct rate to avoid undesirable consequences or complications.
RIGHT DOSE: Always ensure the right dose is administered. Overdosage has dangerous consequences and underdosing may not provide the therapeutic effect intended. The nurse or midwife must pay attention to the units of medications for example milligrams (mg) and micrograms (mcg) as these can be easily interchanged. For certain drugs that require calculated dosages based on weight, make sure the correct weight is taken and the calculation is also verified by another nurse. Other drugs also require reconstitution and therefore the nurse must ensure the right and correct amount of diluent is used.
OTHER “RIGHTS” (R’s) OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION
RIGHT PATIENT EDUCATION: The nurse or midwife must ensure that the patient understands what the medication is for. Explain to them the action of the drugs and various side effects. Make them aware they should contact the nurse on duty if they experience side-effects or reactions.
RIGHT DOCUMENTATION: Make sure you sign after administering the medication indicating your remarks as well.
RIGHT TO REFUSE: Make sure you have the patient consent to administer medications. It is important to note that patients do have a right to refuse medication if they have the capacity to do so except in certain situations (certain mental illnesses)
RIGHT ASSESSMENT: Check the client’s history of drug interactions, allergies, and contraindications. Check your patient actually needs the medication. Check Baseline observations such as Vital signs where necessary.
RIGHT EVALUATION: Monitor to see medication is working the way it should and observe patient continuously when required. Ensure medications are reviewed regularly
Discover more from Nursing In Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Notes
Understanding Hypotension: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
Hypotension, commonly referred to as “low blood pressure,” is a medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is lower than normal (when the blood pressure reading is lower than 90/60mmHg). There are various types of hypotension, each with different causes, symptoms, and treatments. As a nurse, it is important to be aware of the different types of hypotension and their management in order to provide safe and effective care to your patients.
Orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension is a type of hypotension that occurs when a person changes position from lying down or sitting to standing up. This can cause a sudden drop in blood pressure, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting. Orthostatic hypotension is common in older adults, especially those with underlying medical conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, or autonomic neuropathy.
The management of orthostatic hypotension involves lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding sudden changes in position, staying hydrated, and wearing compression stockings. Medications such as fludrocortisone, midodrine, and droxidopa may also be prescribed to help raise blood pressure.
Neurally mediated hypotension.
Neurally mediated hypotension also known as the fainting reflex, neurocardiogenic syncope, vasodepressor syncope, the vaso-vagal reflex, and autonomic dysfunction is a type of hypotension that occurs in response to certain triggers, such as standing for a long time or exposure to heat. It is caused by a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates blood pressure and heart rate. Neurally mediated hypotension can cause symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, and fainting. Other symptoms may include confusion, muscle aches, headaches, and chronic fatigue.
The treatment of neurally mediated hypotension involves avoiding triggers and increasing fluid and salt intake.
Severe hypotension
Severe hypotension is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment. It is characterized by a sudden and severe drop in blood pressure, which can lead to organ damage and even death if not promptly addressed. Severe hypotension can be caused by various conditions, such as sepsis, anaphylaxis, or a heart attack.
The management of severe hypotension involves identifying and treating the underlying cause. This may involve administering intravenous fluids, medications such as vasopressors or inotropes, and oxygen therapy. In severe cases, mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be necessary.
Postprandial hypotension
It is common in older adults and those with underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, or autonomic neuropathy. Postprandial hypotension is a type of hypotension that occurs after eating a meal. After eating, the heart rate ramps up to send blood flowing to the digestive system, but with this type of low blood pressure, the mechanism fails, resulting in dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting.
The management of postprandial hypotension involves eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding large meals high in carbohydrates or fats. Medications such as acarbose, midodrine, and caffeine may also be prescribed.
Discover more from Nursing In Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Notes
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE), A COMMONLY MISDIAGNOSED MEDICAL CONDITION
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various organ systems in the body. It is characterized by the production of autoantibodies against self-antigens, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage including the joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, brain, heart, and lungs. SLE is a heterogeneous disease with a wide range of clinical manifestations, making it difficult to diagnose and manage.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
The pathophysiology of SLE involves a complex interplay between genetic, environmental, hormonal, and immunologic factors. Multiple genetic loci have been associated with SLE, including genes involved in immune system function and regulation. Environmental factors such as infections, medications, and ultraviolet light exposure have also been implicated in the development of SLE.
In SLE, immune dysregulation leads to the production of autoantibodies against nuclear components such as DNA, RNA, and histones. These autoantibodies form immune complexes that deposit in various tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Additionally, immune dysregulation can lead to aberrant T-cell activation, cytokine production, and complement activation, further contributing to the pathogenesis of SLE.
CAUSES
The exact causes of SLE are not fully understood, but a combination of genetic, environmental, hormonal, and immunologic factors are thought to contribute to its development. Women are more commonly affected than men, and the disease often presents during the childbearing years. Genetic factors are estimated to account for up to 66% of the risk for developing SLE. Environmental factors such as infections, medications, and ultraviolet light exposure have also been implicated in the development of SLE.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
The clinical manifestations of SLE are diverse and can affect multiple organ systems in the body. Common symptoms include fatigue, fever, joint pain and swelling, skin rashes, and photosensitivity. SLE can also cause more serious complications such as lupus nephritis, which is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with SLE.
ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSTIC FINDINGS
The diagnosis of SLE is based on a combination of clinical and laboratory findings. The American College of Rheumatology has developed diagnostic criteria for SLE, which require the presence of at least four of the following: malar rash, discoid rash, photosensitivity, oral ulcers, arthritis, serositis, renal disorder, neurologic disorder, hematologic disorder, immunologic disorder, and antinuclear antibody positivity. Laboratory tests that may be helpful in diagnosing SLE include antinuclear antibody (ANA) testing, anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibody testing, and complement-level testing.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
The management of SLE involves a multidisciplinary approach, including rheumatologists, nephrologists, dermatologists, and other specialists as needed. Treatment goals include controlling disease activity, preventing flares, and minimizing organ damage. Treatment options may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antimalarial drugs, glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, and biological agents.
PHARMACOLOGIC MANAGEMENT
Pharmacologic management of SLE involves a range of medications targeting different aspects of the disease’s pathophysiology. NSAIDs can be used to manage mild to moderate pain and inflammation, while antimalarial drugs such as hydroxychloroquine can be used to prevent disease flares and reduce disease activity. Glucocorticoids such as prednisone can be used to manage severe disease activity and organ involvement, but their long-term use is associated with significant adverse effects. Immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclophosphamide can be used to control disease activity and prevent organ damage. Biologic agents such as belimumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting B-cell activating factor, have also been approved for the treatment of SLE.
Systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis and management, https://academic.oup.com/rheumatology/article/56/suppl_1/i3/2738661.
C. (2023, January 31). Systemic lupuserythematosus (SLE). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/lupus/facts/detailed.html
Systemic lupus erythematosus pathophysiology – wikidoc. (n.d.). Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Pathophysiology – Wikidoc. https://www.wikidoc.org/index.php/Systemic_lupus_erythematosus_pathophysiology
Discover more from Nursing In Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Notes
TYPES OF SHOCK
Shock is a threatening life condition of circulatory failure which causes inadequate oxygen delivery to meet cellular metabolic needs and oxygen consumption requirements, producing cellular and tissue hypoxia. The effects of shock are initially reversible, but rapidly become irreversible, resulting in multiorgan failure (MOF) and death. When a patient presents with undifferentiated shock, it is important that the clinician immediately initiate therapy while rapidly identifying the etiology so that definitive therapy can be administered to reverse shock and prevent MOF and death.
There are four main types of shock:
1. Anaphylactic shock
2. Cardiogenic shock
3. Hypovolemic shock
4. Septic shock
Anaphylactic shock is a severe and sudden allergic reaction that can occur after exposure to an allergen. Symptoms include swelling of the face and throat, difficulty breathing, and a drop in blood pressure. Anaphylactic shock can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical treatment.
Cardiogenic shock occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can be due to a heart attack, heart failure, or other heart conditions. Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, and a weak and irregular heartbeat. Cardiogenic shock is a medical emergency and requires treatment in a hospital.
Hypovolemic shock occurs when there is a decrease in the amount of blood or fluid in the body. This can be due to blood loss from an injury, severe dehydration, or excessive vomiting or diarrhea. Symptoms include lightheadedness, fainting, and a decrease in urine output. Hypovolemic shock can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical treatment.
Septic shock. This type of shock is caused by an infection or sepsis. Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when an infection spreads throughout the body. Symptoms include low blood pressure, rapid heart rate, chills, and fever. Septic shock is a medical emergency and requires treatment in a hospital.
Discover more from Nursing In Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
-

 Nursing News5 years ago
Nursing News5 years agoLIST OF ACCREDITED GOVERNMENT NURSING AND MIDWIFERY TRAINING SCHOOLS IN GHANA
-

 Nursing News3 years ago
Nursing News3 years agoNURSING ADMISSION FORMS ON SALE FOR THE 2023/2024 ACADEMIC YEAR
-

 Nursing Procedures and Skills5 years ago
Nursing Procedures and Skills5 years agoTHE NURSES PLEDGE AND THE MIDWIVE’S PRAYER
-

 Nursing Procedures and Skills5 years ago
Nursing Procedures and Skills5 years agoNURSING TRAINING ADMISSION INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
-

 Nursing News4 years ago
Nursing News4 years agoGHS INTRODUCES TWO NEW BELT COLOURS FOR TWO NEW LEVELS IN THE NURSING AND MIDWIFERY SERVICE
-

 Nursing News4 years ago
Nursing News4 years agoMOH SUSPENDS THE 2021/2022 ACADEMIC CALENDAR FOR NURSING AND MIDWIFERY SCHOOLS
-
 Notes5 years ago
Notes5 years agoCOMMON TYPES OF INTRAVENOUS (IV) FLUIDS AND THEIR USES
-

 Nursing News5 years ago
Nursing News5 years agoLIST OF PRIVATE NURSING AND MIDWIFERY TRAINING SCHOOLS (ACCREDITED)