Nursing Procedures and Skills
THE PATIENT’S CHARTER – PATIENT’S RIGHTS AND RESPONSIBILITIES

The Patients’ Charter is an official document by an organization or government that enlists the Rights of the patient and their Responsibilities. Hospitals and other healthcare facilities are therefore expected to respect the rights of patients/clients and family. The Patient Charter is to enable the patient and their relatives to understand their Rights and Responsibilities.
PATIENT’S RIGHTS
- The patient has the right to quality basic health care irrespective of his/her geographical location.
- The patient is entitled to full information on his/her condition and management and the possible risks involved except in emergency situations when the patient is unable to decide and the need for treatment is urgent.
- The patient is entitled to know of alternative treatment(s) and other health care providers within the Service if these may contribute to improved outcomes.
- The patient has the right to know the identity of all his/her caregivers and other persons who may handle him/her including students, trainees, and ancillary workers.
- The patient has the right to consent or decline to participate in a proposed research study involving him or her after a full explanation has been given. The patient may withdraw at any stage of the research project.
- A patient who declines to participate in or withdraws from a research project is entitled to the most effective care available.
- The patient has the right to privacy during consultation, examination, and treatment. In cases where it is necessary to use the patient or his/her case notes for teaching and conferences, the consent of the patient must be sought.
- The patient is entitled to confidentiality of information obtained about him or her and such information shall not be disclosed to a third party without his/her consent, or the person entitled to act on his/her behalf except where such information is required by law or is in the public interest.
- The patient is entitled to all relevant information regarding policies and regulations of the health facilities that he/she attends.
- Procedures for complaints, disputes, and conflict resolution shall be explained to patients or their accredited representatives.
- Hospital charges, mode of payments, and all forms of anticipated expenditure shall be explained to the patient prior to treatment.
- Exemption facilities, if any, shall be made known to the patient.
- The patient is entitled to personal safety and reasonable security of property within the confines of the Institution.
- The patient has the right to a second medical opinion if he/she so desires.
PATIENT’S RESPONSIBILITIES
The patient should understand that he/she is responsible for his/her own health and should therefore co-operate fully with healthcare providers. The patient is responsible for:
- Providing full and accurate medical history for his/her diagnosis, treatment, counseling, and rehabilitation purposes.
- Requesting additional information and or clarification regarding his/her health or treatment, which may not have been well understood.
- Complying with prescribed treatment, reporting adverse effects, and adhering, to follow-up requests.
- Informing his/her healthcare providers of any anticipated problems in following prescribed treatment or advice.
- Obtaining all necessary information, which have a bearing on his/her management and treatment including all financial implications.
- Acquiring knowledge, on preventive, promotive and simple curative practices and where necessary to seeking early professional help.
- Maintaining safe and hygienic environment to promote good health.
- Respecting the rights of other patients/clients and Health Service personnel
- Protecting the property of the health facility.
Discover more from Nursing In Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Nursing Procedures and Skills
Essential Strategies for Dealing with Difficult Patients and Families in Healthcare Settings

As nurses, we sometimes encounter patients and their families who are difficult to work with. These individuals may be demanding, uncooperative, or even hostile. While these situations can be challenging, we must develop strategies to handle them effectively. Here are a few of the approaches to handling difficult patients and relatives:
Understand the Patient’s Background
It is important to understand that difficult behavior may be a result of the patient’s underlying condition, personality, or previous experiences. For example, patients who are in pain, anxious, or feeling vulnerable may be more likely to act out. It is therefore important for the nurse to try to understand the patient’s background and perspective and tailor your approach accordingly.
Be Calm and Stay Objective.
It is essential for the nurse to remain composed and calm when dealing with difficult patients. This will help you maintain control of the situation and prevent it from escalating. It is also important for nurses to remain objective and not take patients’ and relatives’ behavior personally when dealing with their difficult behavior. Try to focus on the patient’s needs and the care that you are providing, rather than getting caught up in their emotional reactions.
Show Empathy
Empathy is one of the essential qualities of a nurse. It is an important skill when dealing with difficult patients and their families. Showing empathy means acknowledging the patient’s feelings and concerns and trying to see the situation from their perspective. The nurse can use phrases like “I understand how you feel” or “I’m sorry you’re going through this” to demonstrate empathy.
Use Effective Communication Techniques
Effective communication is key when dealing with difficult patients and their relatives. Make an effort to listen actively to the patient or family member’s concerns. Use active listening skills, such as repeating back what the patient has said to ensure you have understood their concerns correctly. Using open-ended questions encourages the patient to talk and express their concerns. This will show that you care about their needs and are willing to work with them.
Know When to Seek Help
It’s important to know when to seek help from colleagues or a supervisor. If you are feeling overwhelmed or unable to manage a difficult patient or family member, don’t hesitate to ask for assistance from colleagues or a supervisor.
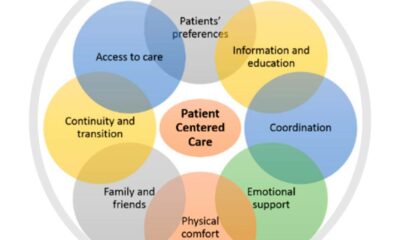
Involve the Patient in their Care
The patient is at the center of care. Empowering the patient and involving them in their care can help reduce difficult behavior. Encourage the patient to participate in their care plan, and explain the reasoning behind any treatments or interventions. This can help allay the client’s anxiety.
Discover more from Nursing In Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Lifestyle
HOW TO COMMUNICATE EFFECTIVELY WITH PATIENTS

Effective communication with patients is a crucial aspect of healthcare. It allows healthcare providers to establish trust and rapport with their patients, gather accurate information about their health concerns, and provide effective treatment and follow-up care. In this article, we will discuss some key strategies for effective communication with patients.
First, it is important to establish a warm and welcoming environment for patients. This can be achieved through nonverbal cues such as maintaining eye contact, smiling, and using a friendly tone. It is also important to give patients your undivided attention and to listen actively to what they have to say. This includes using techniques such as rephrasing and clarifying to ensure that you have accurately understood the patient’s concerns.
It is also important to communicate clearly, concisely, and respectfully. This means using simple, easy-to-understand language and avoiding jargon or technical terms that may be confusing to patients. It is also important to be patient and allow the patient to ask questions or express any concerns they may have.
In addition to verbal communication, it is important to consider nonverbal cues as well. This includes maintaining appropriate physical boundaries and using appropriate touch. Nonverbal cues can also be used to show empathy and support, such as by nodding or maintaining a comforting facial expression.
Another important aspect of effective communication with patients is cultural competency. It is important to be sensitive to the cultural and linguistic backgrounds of patients and to take steps to ensure that they feel respected and understood. This may include using interpreters or translation services or simply taking the time to learn about and respect the cultural beliefs and practices of the patient.
Effective communication with patients is not only important for the provision of quality healthcare, but it is also essential for building trust and rapport with patients. By following the strategies outlined above, healthcare providers can improve their communication skills and provide the best possible care for their patients.
Discover more from Nursing In Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Nursing Procedures and Skills
IMPROVING NURSE-PATIENT RELATIONSHIP

Improving the nurse-patient relationship is essential for providing high-quality healthcare and ensuring positive patient outcomes. A strong nurse-patient relationship can lead to increased trust, improved adherence to treatment plans, and a more positive work environment for nurses. The following are ways for improving the nurse-patient relationship:
Communicate effectively: Effective communication is key to building a strong relationship with patients. This means listening actively to what patients have to say, using clear and straightforward language, and providing information in a way that is easy for patients to understand.
Show empathy: Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. By showing empathy, nurses can help patients feel heard and supported, which can improve the relationship and lead to better patient outcomes.
Be respectful: Treating patients respectfully is an important part of building a strong relationship with them. This means showing respect for their autonomy, privacy, and dignity, and treating them as partners in their own care.
Be responsive: Patients may have questions or concerns at any time, and it is important for nurses to be responsive to their needs. This means being available to answer questions and address concerns and making sure patients have the information they need to make informed decisions about their care.
Collaborate with other healthcare providers: Nurses often work with other healthcare providers, such as doctors, therapists, and social workers, to provide comprehensive care for patients. By collaborating with these providers, nurses can ensure that patients receive the best possible care and support.
Involve patients in their care: Involving patients in their own care can help improve the nurse-patient relationship. This means giving patients the opportunity to participate in decision-making and allowing them to express their preferences and concerns.
By implementing these tips, nurses can improve the nurse-patient relationship and provide better care for their patients. A strong nurse-patient relationship can lead to better outcomes and a more positive healthcare experience for everyone involved.
Discover more from Nursing In Ghana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
-

 Nursing News5 years ago
Nursing News5 years agoLIST OF ACCREDITED GOVERNMENT NURSING AND MIDWIFERY TRAINING SCHOOLS IN GHANA
-

 Nursing News3 years ago
Nursing News3 years agoNURSING ADMISSION FORMS ON SALE FOR THE 2023/2024 ACADEMIC YEAR
-

 Nursing Procedures and Skills5 years ago
Nursing Procedures and Skills5 years agoTHE NURSES PLEDGE AND THE MIDWIVE’S PRAYER
-

 Nursing Procedures and Skills5 years ago
Nursing Procedures and Skills5 years agoNURSING TRAINING ADMISSION INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
-

 Nursing News4 years ago
Nursing News4 years agoGHS INTRODUCES TWO NEW BELT COLOURS FOR TWO NEW LEVELS IN THE NURSING AND MIDWIFERY SERVICE
-

 Nursing News4 years ago
Nursing News4 years agoMOH SUSPENDS THE 2021/2022 ACADEMIC CALENDAR FOR NURSING AND MIDWIFERY SCHOOLS
-
 Notes5 years ago
Notes5 years agoCOMMON TYPES OF INTRAVENOUS (IV) FLUIDS AND THEIR USES
-

 Nursing News5 years ago
Nursing News5 years agoLIST OF PRIVATE NURSING AND MIDWIFERY TRAINING SCHOOLS (ACCREDITED)